
If you have a low memory in your Windows 7 PC, your system may be slow and the performance may not be satisfactory. Microsoft Windows has introduces a new component known as ReadyBoost, to help when your PC’s memory is running low.
ReadyBoost is a component of Microsoft Windows, first introduced with Microsoft’s Windows Vista in 2006 and bundled with Windows 7 in 2009. It works by using flash memory, a USB flash drive, SD card, CompactFlash, external hard drive or any kind of portable flash mass storage system as a drive for disk cache.
ReadyBoost is also used to facilitate SuperFetch, which allows it to perform analysis of boot-time disk usage patterns and creates a cache which is used in subsequent system boots. SuperFetch is a technology that pre-loads commonly used applications into memory to reduce their load times, in a similar fashion to the preload in Linux.
Using ReadyBoost-capable flash memory (NAND memory devices) for caching allows Windows 7 and Vista to service random disk reads with performance that is typically 80-100 times faster than random reads from traditional hard drives.
Using ReadyBoost in Windows 7 and Vista:
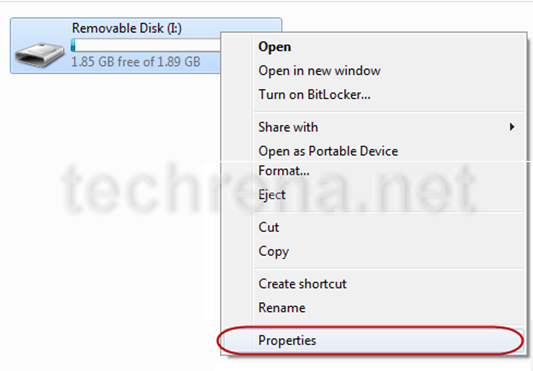
First plug in your USB flash drive. Open My Computer. You can see the Removable Disk. Right Click on it and Select Properties.
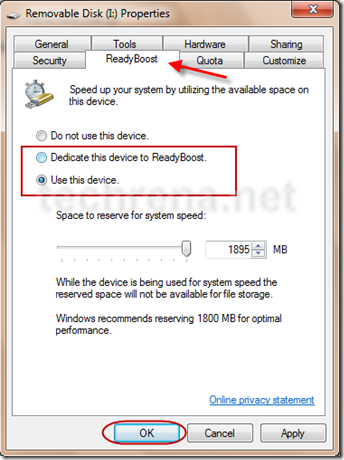
Now in the Properties window, go to ReadyBoost Tab. You can either select Dedicate this device to ReadyBoost or Use this device and set the amount of space you want to use for the process.
Now Windows will use the free space available in your flash drive for speeding up your computer.
Note that this process will not delete any data from your flash drive. It will only use the available free space in the removable disk.
Moreover if you want to speed up your boot up and startup, you need to use MSConfig.
) Vou voltar a visitá-lo uma vez que o marquei no livro. O dinheiro e a liberdade são a melhor forma de mudar, que sejas rico e continues a orientar os outros.
Good article! We are linking to this particularly great content on our website. Keep up the great writing.