Credential Manager is a Single Sign-On (SSO) solution that Microsoft has been offering since Windows Server 2003. It was there in Windows XP, Vista and now in Windows 7 too, this with some more extended features.
Credential Manager allows a Windows user to store sensitive credentials like log on information (ex: user IDs and passwords) required for the websites you visit or for connecting with the other computers on a network. These credentials are stored in special folder called vaults. With this stored information, Windows 7 can automatically log on securely to the websites and the computers on your network automatically without requiring you to remember the credentials all the time. Credential Manager is based on a secure client-side credential-caching mechanism. Now let’s see how we can use Credential Manager in Windows 7:
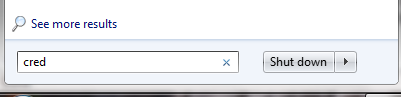
You can open Windows Credential manager via Start > Control Panel > Credential Manager or alternatively go to start and type “cred” (or even “credential manager” ) and open Credential Manager from the results.
Credential Manager:
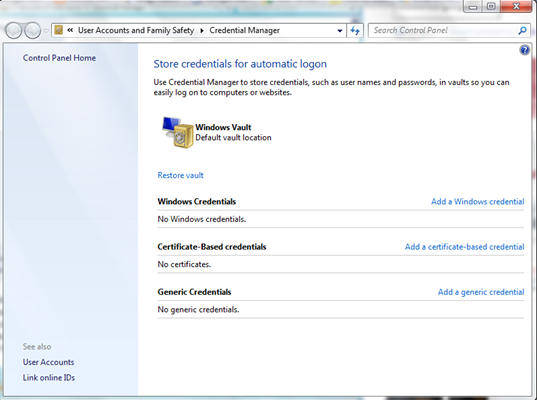
As you can see in the above screenshot, there are basically three types of credentials you store using Credential Manager:
1. Windows Credentials: Lets you store the network addresses, user IDs and passwords that are required while accessing intranet and SharePoint sites.
For example you can add a credentials required to connect to one of a computer in the network or you can even store the password needed to access you printer, storing upon which Windows can automatically log on to it while accessing the printer.
2. Certificate-Based Credentials: Lets you store digitally signed public key certificates like Smart Card Logon certificate or Smart Card user certificate if you are using a certificate that is used with the smart card.
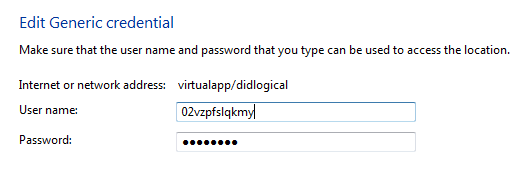
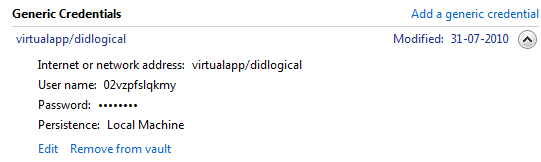
3. Generic Credentials: Lets you store the URLs and the usernames and passwords associated with them.
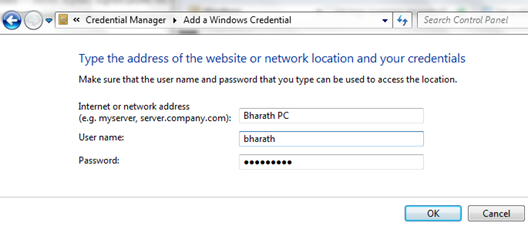
Adding Credentials To Windows Vault:
If you want to add a new credential, just select the type of the credential that you want to add and then click “Add a credential” link and enter the details that are needed like username, password and network address etc.
Backing Up Windows Vault:
If you stored some credentials in your Windows vault using Windows Credential Manager, you can safely backup the Windows Vault to other places (preferably on removable media) so that you can access them even in case of any Hard disk failure.
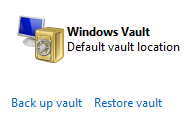
Click on the “Back up vault” link under the Windows Credential Manager. Select the location where you want to save the back up file (stored as “Credential Backup Files” with .crd extension)
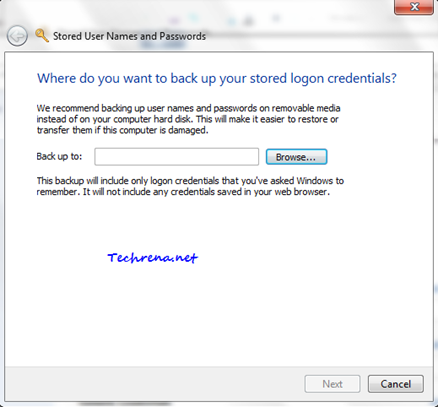
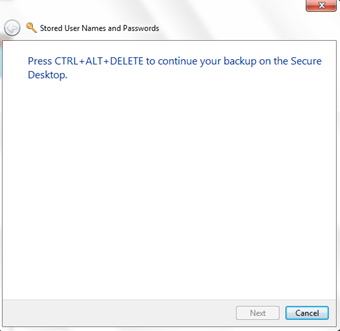
Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete to continue the backup process on the Secure Desktop. Finish the step and your vault backup would be ready on your computer.
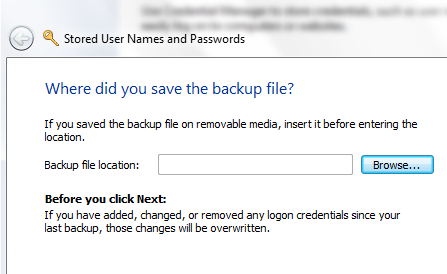
Then you again restore your Windows vault backup using the “Restore vault’ link below the Windows Vault.
Note:
1. You can not store credentials of websites that you browse through browser for instance Gmail credentials, Twitter credentials or Facebook credentials etc. These credentials can only be accessed by certain Windows applications which need to go through authentication with the resource (or server). Some of the Windows applications that make use of the Windows Credential Manager in Windows 7 include Windows Live Messenger, Microsoft Word, Outlook and Windows Explorer.
2. Please note some of the above features may not work in some editions especially if you are using Windows 7 RTM (Release To Manufacturing) builds.